blob-article
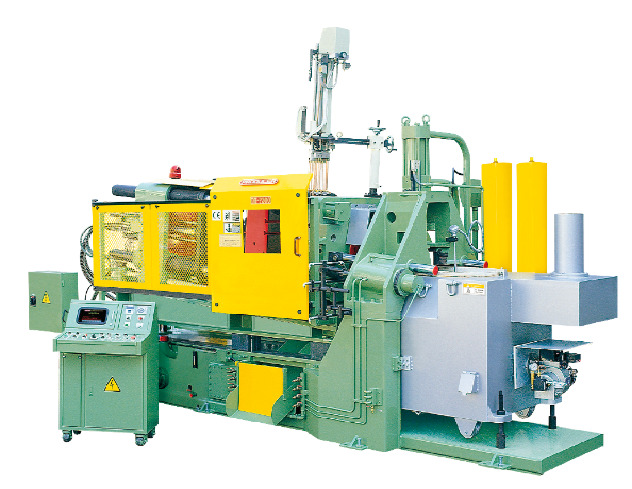

Die Casting is an exceptionally proficient and versatile assembling strategy where liquid metal is constrained into a form to deliver complicated and exact parts. This innovation has filled in fame across various businesses because of its capacity to deliver great parts with confounded calculations and tight resiliences. In this blog article, we will take a gander at the basic capability of kick the bucket projecting in various ventures, featuring its applications, advantages, and commitments to contemporary assembling.
What is Die Casting ?
Die Casting is a metal projecting technique that utilizes enormous strain to drive liquid metal into a form. Passes on, or molds, are framed of steel or other strong materials that might be utilized over and again. This approach can make convoluted shapes that are troublesome or difficult to make with run of the mill projecting systems.
Process Steps
-
Mould Design: The first step in die casting is to design the mould, which must take into account the metal's thermal expansion and the intended final shape.
-
Melting the Metal: The metal (usually aluminium, zinc, or magnesium) is melted in a furnace.
-
Injection: Molten metal is poured into the mould cavity under high pressu2e, ensuring complete filling and reducing air pockets.
-
Cooling: The metal cools and hardens within the mould.
-
Ejection: After cooling, the die opens and the finished part is ejected.
Types of Die Casting
1.Hot Chamber Die Casting :
- The furnace and injection mechanism are linked, allowing molten metal to be injected straight into the die.Commonly used for metals with low melting points, such as zinc and lead.
2.Cold Chamber Die Casting:
-
Molten metal is pumped into a separate chamber before being fed into the die. Used for metals with higher melting points, such as magnesium and aluminium.
3.Vacuum Die Casting:
-
Vacuum die casting is a form of high-pressure die casting in which air is removed from the die chamber before molten metal is poured. The vacuum decreases or eliminates trapped gases in the final casting, resulting in higher part density and mechanical characteristics.
4.Gravity Die Casting :
- Gravity pass on projecting, otherwise called extremely durable shape projecting, is the method involved with emptying liquid metal into a metal form (or kick the bucket) utilizing gravity alone. The metal streams into the form, making up for the shortfall prior to cooling and solidifying.
The Role of Die Casting in Various Industries
1. Auto Industry :
-
Motor parts, gearbox lodgings, primary pieces and elaborate components.The auto area benefits from kick the bucket projecting's capacity to cause lightweight parts that to further develop eco-friendliness while keeping up with strength. With the ascent of electric vehicles, there is an expanded interest for lightweight materials, which drives the interest for bite the dust cast parts.
2. Consumer Electronics :
-
Die casting allows producers to create elegant, visually appealing products while retaining great precision. The high-quality finish minimises the need for extra surface treatments, resulting in quicker manufacturing times.
3. Industrial Equipment :
- Die-cast components are known for their durability and strength, which are essential in high-demand industrial applications. The cost-effective manufacturing procedure enables the creation of complex parts that enhance machinery performance.
4. Medical Devices :
-
Precision and dependability are critical in medical manufacturing. Die casting enables the production of very precise components that fulfil stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring safety and efficacy.
5. Energy Sector :
- Die casting supports the development of efficient and sustainable energy solutions. Lightweight components improve energy production efficiency, contributing to the overall sustainability goals of the energy sector.
Advantages of Die Casting
-
High Precision: Die casting may achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm, making it excellent for components with precise dimensions.
-
Surface Finish: The die casting technique enables the rapid manufacture of large quantities of parts, resulting in shorter lead times.
-
Efficiency: The die casting technique enables the rapid manufacture of large quantities of parts, resulting in shorter lead times.
-
Complex Shapes : Die casting may produce elaborate shapes and features, such as thin walls and complicated geometries.
-
Material Versatility: Metal alloys such as aluminium, zinc, magnesium, and copper can all be employed.
Advanced Applications and Innovations
3D Printing reconciliation:
The mix of kick the bucket projecting and 3D printing innovation empowers quick prototyping and the manufacture of convoluted shape plans that would be hard to create utilizing conventional strategies.
Savvy Assembling :
Incorporating IoT and robotization into pass on projecting tasks increments productivity, dispenses with squander, and works on quality control through continuous checking.
Reasonable Practices:
Progressions in reusing processes and the utilization of harmless to the ecosystem materials are impacting the fate of pass on projecting, making it a more manageable option for producers.
Challenges in Die Casting
High initial tooling costs :
Creating long-lasting, accurate moulds is expensive, therefore, die casting is best suited for high-volume production runs. However, in mass production, the cheap unit cost per item offsets these costs.
Porosity and imperfections:
Air caught in the shape can cause porosity in the completed thing, bringing down its solidarity. High level cycles, for example, vacuum pass on projecting, help to lighten this issue.
Design Limitations :
Die casting moulds are limited by the requirement for consistent wall thickness and draft angles to aid with part ejection. Certain intricate designs may not be possible without further post-casting machining.